Inject-A-Lume for in vivo Products
| Cat# | Name | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

| 303-INJ | Injectable native Coelenterazine, highly pure (99.7%) and op ... | 
Injectable native Coelenterazine, highly pure (99.7%) and optimized for in vivo research.
Recommended path of injection: intra-peritoneal cavity. For animal use only. | |||||||||||

| 301-INJ | Injectable h-Coelenterazine, highly pure (99%) and optimized ... | 
Injectable h-Coelenterazine, highly pure (99%) and optimized for in vivo research.
Benzyl Coelenterazine (h-CTZ) in sterile injection vials with a low retention volume. Each kit is supplied with two ‘Inject-A-Lume’ vials of 500 µg h-CTZ and a sterile ‘Fuel-Inject’ diluent. For animal use only. | |||||||||||
| 355-INJ | e-CTZ is now available in sterile injection vials with a low ... | 
e-CTZ is now available in sterile injection vials with a low retention volume. Each kit is suppled with two ‘Inject-A-Lume’ vials of 500 ug e-CTZ and 500 ul of steril ‘Fuel-Inject’ diluent. It was reported that this analogue enhances the signal by two-fold in Renilla Luciferase in vivo studies.
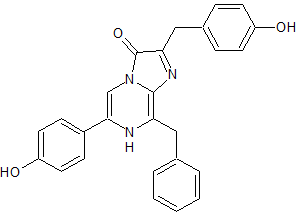
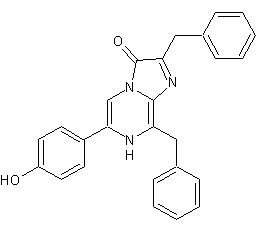
e-coelenterazine or Coelenterazine-E (e-CTZ) is a synthetic analogue of native Coelenterazine with an additional ethyl group, forming an additional ring system. First described by Shimomura in 1989. For Renilla muelleri Luciferase, an increase of 750% in initial intensity and 137% in total light was observed using e-Coelenterazine compared to naitve Coelenterazine.
Note: In will not be utilized by Gaussia Luciferase. |



 Coelenterazine (native-CTZ) in sterile injection vials with a low retention volume. Each kit is supplied with two ‘Inject-A-Lume’ vials of 500 µg CTZ and 500 µl of sterile ‘Fuel-Inject’ diluent.
Coelenterazine (native-CTZ) in sterile injection vials with a low retention volume. Each kit is supplied with two ‘Inject-A-Lume’ vials of 500 µg CTZ and 500 µl of sterile ‘Fuel-Inject’ diluent.